N 2 N 1 x 2 g2-1. 700 600 500 Number of 400 yeast cells 300 200 100 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time in hours a At what point is the rate of population increase the greatest.
Calculus Help And Graphing Wyzant Ask An Expert
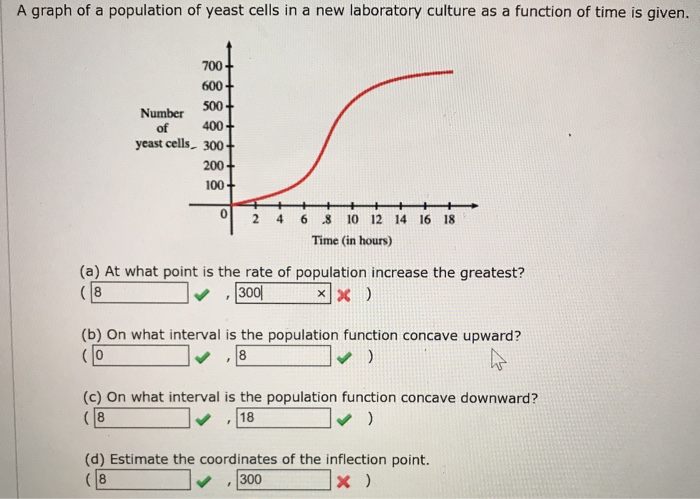
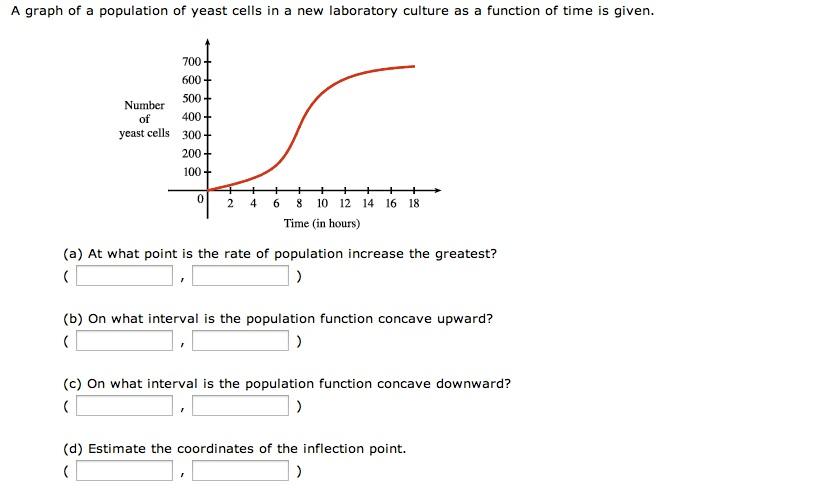
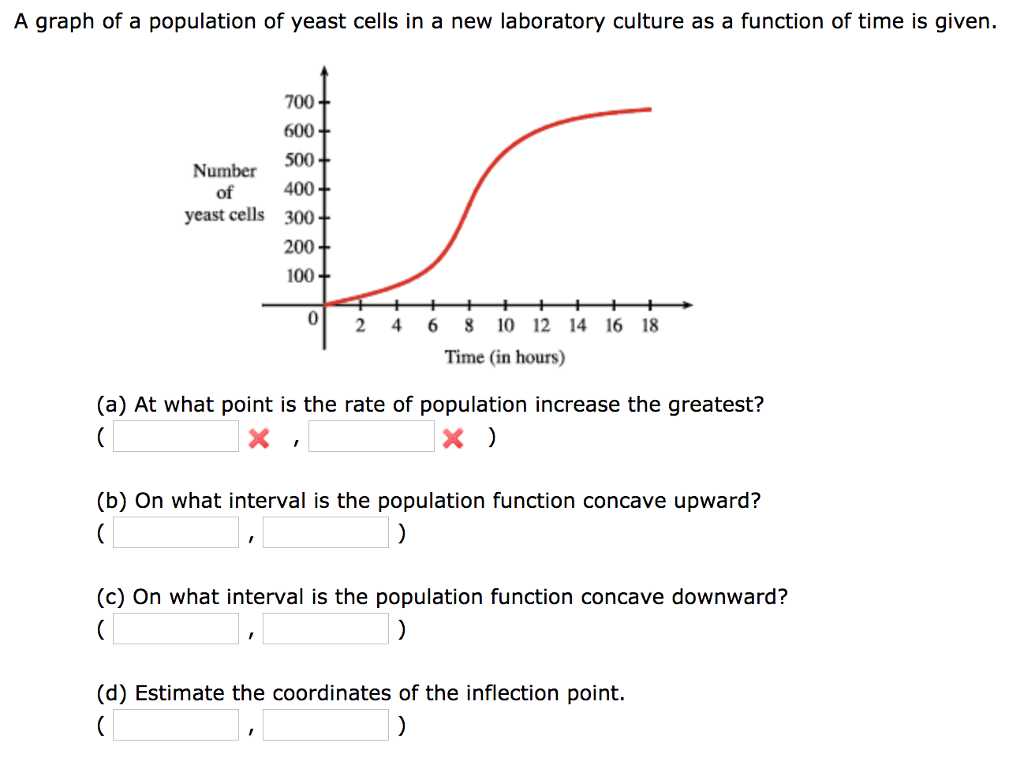
A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time from t 0 to t 18 is shown.
. Classic example is yeast in a champagne bottle. The population of a culture of yeast cells is studied in the laboratory to see the effects of limited resources food space on population growth. What does the graph of P tell us about.
700 600 500 Number of 400 yeast cells 300 200 100 4 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time in hours a Describe how the rate of population increase varies. The number of yeast cells in a laboratory culture increases rapidly initially but levels off eventually. Find the values of a and b.
Shown is the graph of the population function for yeast cells in a laboratory culture. A Make a graph of the yeast population as a function of elapsed time. A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time is shown.
At 2-h intervals the size of the population measured as total mass of yeast cells is recorded. The rate of increase of the population is initially very small then gets larger until it reaches a maximum at about t 8. At time t 0 the population is 30 cells and is increasing at a rate of 18 cellshour.
Consequently after any specific length of time say from t 1 to t 2 the number of cells in the population would be given by the equation. A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time from t 0 to t 18 is shown. Up to 24 cash back This is indicative of the stationary phase in which the population has reached carrying capacity K.
In the first lesson students set up a simple way to indirectly observe and quantify the amount of respiration occurring in yeast-molasses cultures. At the end of the stationary phase or 66 hours the population begins to fall. A yeast growth curve -- a graph depicting stages of population growth and decline in a closed environment.
700 600 500 Number of 400 yeast cells 300 200 100 0 4 2 16 18 8 10 12 14 Time in hours a Describe how the rate of population increase varies. What does the graph of tell us about the yeast population. A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time is given.
Shown is the graph of the population function Pt for yeast cells in a laboratory culture. This lesson is the second of two that explore cellular respiration and population growth in yeasts. The rate of increase of the.
4 10 12 14 16 18 Time in hours a Describe how the rate of population increase varies. Use the method of Example I to graph the derivative. The number of yeast cells in a laboratory culture increases rapidly initially but levels off eventually.
700 600 500 Number of 400 yeast cells 300 200 - 100 4 6 10 12 14 16 18 Time in hours a Describe how the rate of population increase varies. In other words the population of cells would double in number with each generation. What does the graph of P tell us about the yeast population.
A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time from t 0 to t 18 is shown. A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory Shown is the graph of traffic on an Internet service providers T1 Use Simpsons Rule to estimate the total amount of data transmitted during that time period. The rate of increase of the population is initially very small then gets larger until it reaches a maximum at abou t 8.
700 600 500 Number of 400 yeast cells 300- 200 100 2. Find the values of a and b. This means that the population has reached the point where for whatever reason eg.
A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time from t 0 to t 18 is shown. The population is modeled by the function n ft a 1 be07t where t is measured in hours. The population is modeled by the function nfta1be-07t where t is measured in hours.
Yeast-beasties continue to reproduce until concentration of alcohol yeast piss and carbon dioxide the sparkle in traditionally-made champagne but lethal morning breath to another yeast poisons them. O The rate of increase of the population is initially very large then gets smaller until it reaches a. D Estimate the coordinates of the inflection point.
It grows the fastest when it is about halfway to its maximum population. Based on questions that arose during the first lesson and its associated activity students in this lesson work in small. It grows the fastest when it is about halfway to its maximum population.
700 600 500 Number of 400 yeast cells 300 200 100 0 24 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time in hours a Describe how the rate of population Increase varles The rate of increase of the population is consistently small. Shown is the graph of the population function Pt for yeast cells in a laboratory culture. Where N 1 is the original number of cells present at time t 1 N 2 is the number of cells present at t 2 and g is the.
O The rate of increase of the population is initially very large then gets smaller until it reaches a minimum at about t 8. Use the method of Example 1 to graph the derivative Pt. A graph of a population of yeast cells in a new laboratory culture as a function of time from t 0 to t 18 is shown.
Use the method of Example I to graph the derivative Pt. At time t 0 the population is 20 cells and is increasing at a rate of 12 cellshour. B When is the rate highest.
C On what intervals is the population function concave upward or downward. Nutrients or space the medium cannot support any more yeast cells. B On what interval is the population function concave upward.
A Describe how the rate of population increase varies.

Solved A Graph Of A Population Of Yeast Cells In A New Chegg Com
Solved A Graph Of A Population Of Yeast Cells In A New Chegg Com
Solved A Graph Of A Population Of Yeast Cells In A New Chegg Com
0 Comments